Disease Area, Infectious Disease V
Product Name: VX-478 l HIV-1 protease inhibitor (#C8947-5)
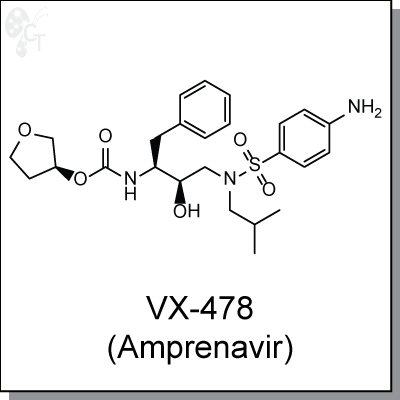
Amprenavir (Agenerase, VX-478), is an orally-available, sulfonamide-based inhibitor of HIV-1 protease, with
relatively weak potency towards HIV-2, at IC50 values of 0.6 and 19 nM, respectively. [1] Similar to other
HIV-1 protease inhibitors, Amprenavir binds to the active site of HIV-1 and inhibits the processing of the gag
and gag-pol polyprotein precursors. The drug concentration of Amprenavir required to reduce viral production
by 50% (IC50) against HIV-1 strain IIIB was 0.08 uM in acutely infected cells and 0.41 uM in chronically
infected cells. Using a different cell line derived from a human T-cell lymphoma, the IC90 of Amprenavir
against HIV-1 strain IIIB was 0.079 uM. [1]
Human dose-escalation studies showed that Amprenavir was well tolerated at single doses up to 1200 mg
with minimal effect on absorption by food administration, unlike with other protease inhibitors such as
indinavir, nelfinavir, and saquinavir. [2]
|
Details
|
Chemical Formula:
|
|
C25H35N3O6S
|
|
CAS No.:
|
|
161814-49-9
|
|
Molecular weight:
|
|
505.63
|
|
Purity:
|
|
> 98%
|
|
Appearance:
|
|
White
|
|
Chemical name:
|
|
(3S)-oxolan-3-yl N-[(2S,3R)-3-hydroxy-4-[N-(2-methylpropyl)(4-aminobenzene)
sulfonamido]-1-phenylbutan-2-yl]carbamate
|
|
Solubility:
|
|
Up to 30 mM in DMSO
|
|
Synonyms:
|
|
VX-478, VX478, Amprenavir, Agenerase
|
|
Storage:
|
|
For longer shelf life, store solid powder at 4oC desiccated, or DMSO solution
at -20oC
|
1. Fung et al., Amprenavir: a new human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease inhibitor. Clin.
Therapeutics, 2000, 22(5), 549-572. Pubmed ID: 10868554
2. Sadler et al., Safety and pharmacokinetics of amprenavir (141W94), a human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
type 1 protease inhibitor, following oral administration of single doses to HIV-infected adults. Antimicrob.
Angets. Chemother. 1999, 43(7), 1686-1692. Pubmed ID: 10390223
|
Product Name: VX-950 (Telaprevir) l HCV protease inhibitor (#C8995-2s)
.png)
VX-950 (Telaprevir) is an orally-available, highly-selective, reversible, peptidomimetic inhibitor of HCV NS3-
4A protease with an IC50 of 0.35 uM and IC90 of 0.83 uM in an HCV replicon assay [1, 2] In human fetal
hepatocytes with genotype 1a HCV-postive patient serum, VX-950 has an IC50 of 280 uM. [3] VX-950
reduces HCV RNA levels in a time- and dose-dependent manner with IC50s of 0.57, 0.49, 0.21, and 0.14 uM
following a 24-, 48-, 72-, and 120-h incubation.
VX-950 forms a covalent, but reversible complex in a slow-on, slow-ff process with a steady-state inhibition
constant (Ki) of 7 nM. [3] Excellent efficacy with high liver exposure in an HCV NS3-4A mouse model was
observed with VX-950.
|
Details
|
Chemical Formula:
|
|
C36H53N7O6
|
|
CAS No.:
|
|
402957-28-2
|
|
Molecular weight:
|
|
679.85
|
|
Purity:
|
|
> 98%
|
|
Appearance:
|
|
White
|
|
Chemical name:
|
|
(1S,3aR,6aS)-2-((S)-2-((S)-2-cyclohexyl-2-(pyrazine-2-carboxamido)acetamido)-
3,3-dimethylbutanoyl)-N-((S)-1-(cyclopropylamino)-1,2-dioxohexan-3-yl)-
octahydrocyclopenta[c]pyrrole-1-carboxamide
|
|
Solubility:
|
|
Up to 100mM in DMSO
|
|
Synonyms:
|
|
VX-950, VX-950, Telaprevir, Incivek, Incivo
|
|
Storage:
|
|
For longer shelf life, store solid powder at 4oC desiccated, or DMSO solution
at -20oC
|
References
1. Lin et al., VX-950, a novel hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS3-4A protease inhibitor, exhibits potent antiviral
activities in HCv replicon cells. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50(5), 1813-1822. Pubmed ID: 16641454
2. Lin et al., Discovery and development of VX-950, a novel, covalent, and reversible inhibitor of hepatitis C
virus NS3.4A serine protease. Infectious Disorders: Drug Targets, 2006, 6(1), 3-16. Pubmed ID: 16787300
3. Perni et al., Preclinical profile of VX-950, a potent, selective, and orally bioavailable inhibitor of hepatitis C
virus NS3-4A serine protease. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50(3), 899-909. Pubmed ID: 16495249
|
Product Name: Zanamivir |Neuraminidase inhibitor (#C9262-2s)
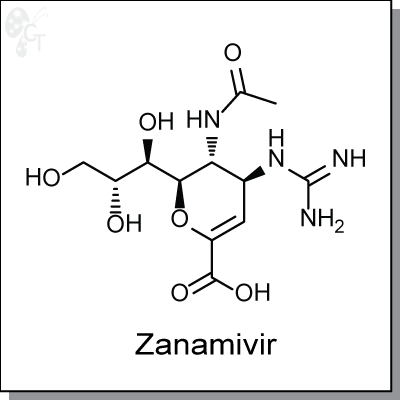
Zanamivir is a dihydropyran-based, sialic acid analog inhibitor of the viral enzyme neuraminidase.
Zanamivir's mode of action is blockage of sialic acid cleavage, thereby preventing further virus distribution.
For type A viruses zanamivir has IC50s of 0.35 nM for the H1N1 subtype, and 1.1 nM for the H3N2 subtype. [1]
In plaque reduction in vitro assays, zanamivir inhibits a wide range of Type A and Type B influenza viruses
with IC50s of plaque formation ranging from 5 to 14 nM in laboratory-passaged strains, and 20 to 1600 nM for
clinical isolates. In human respiratory epithelial cells, EC90s of virus yields were determined to be less than
0.01 ug/mL at 24h for both H1N1 and H3N2 subtypes. [2]
|
|
Details
|
|
|
|
Chemical Formula:
|
|
C12H20N4O7
|
|
CAS No.:
|
|
139110-80-8
|
|
Molecular weight:
|
|
332.31
|
|
Purity:
|
|
> 98%
|
|
Appearance:
|
|
White
|
|
Chemical name:
|
|
(2R,3R,4S)-3-acetamido-4-guanidino-2-((1R,2R)-1,2,3-trihydroxypropyl)-3,4-
dihydro-2H-pyran-6-carboxylic acid
|
|
Solubility:
|
|
Up to 50 mM in DMSO
|
|
Synonyms:
|
|
Relenza, Zanamavir, sialic acid derivative
|
|
Storage:
|
|
For longer shelf life, store solid powder at 4oC desiccated, or DMSO solution
at -20oC
|
References
1. Colman et al., Zanamivir: an influenza neuraminidase inhibitor. Expert Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2005,
3(2), 191-199.
2. Elliott et al., Zanamivir: from drug design to the clinic. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 2001, 356, 1885-1893.
3. McNicholl et al., Neuraminidase Inhibitors: Zanamivir and Oseltamivir. Annals Pharmacother. 2001, 35,
57-70.
|
|

.png)
