Cellular Mechanism, DNA Damage & Repair II
Product Name: Cisplatin | DNA crosslinker (#C2488-10)
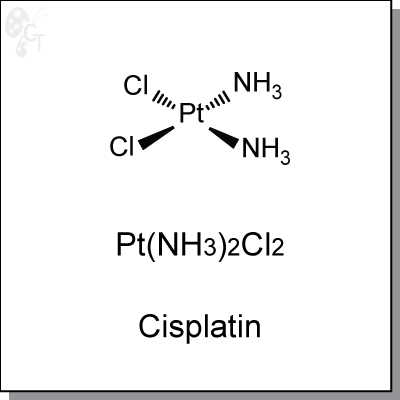
Cisplatin is an intravenously-administered platinum complex that induces cytotoxicity by interference with
transcription and/or DNA replication mechanisms. Cisplatin bind preferentially to guanine, and damages
tumors via induction of apoptosis. [1] DNA binding proteins recognize the topological distortion of DNA and
initiate DNA damage repair, and if repair is not possible, apoptosis.
DNA adducts induced by cisplatin result in activation of several signal transduction pathways, such as ATR,
p53, p73, and MAPK, leading to apoptosis. [2]
NSCLC and colon cancers are resistant to cisplatin, while others such as ovarian cancer acquire resistance
over time. [3]
|
Details
|
Chemical Formula:
|
|
H6CI2N2Pt
|
|
CAS No.:
|
|
15663-27-1
|
|
Molecular weight:
|
|
301.1
|
|
Purity:
|
|
> 98%
|
|
Appearance:
|
|
Yellow
|
|
Chemical name:
|
|
cis-Diammineplatinum(II) dichloride, cis-Dichlorodiammine platinum(II), cis-
Platinum(II) diammine dichloride, Cisplatin
|
|
Solubility:
|
|
Up to N/A in DMSO
|
|
Synonyms:
|
|
Cisplatin, Cisplatinum, CDDP
|
|
Storage:
|
|
For longer shelf life, store solid powder at 4oC desiccated, or store DMSO solution
at -20oC
|
1. Florea et al., Cisplatin as an Anti-Tumor Drug: Cellular Mechanisms of Activity, Drug Resistance and
Induced Side Effects. Cancers 2011, 3, 1351-1371. Pubmed ID: ISSN: 2072-6694
2. Siddik et al., Cisplatin: mode of cytotoxic action and molecular basis of resistance. Oncogene, 2003, 22,
7265-7279. Pubmed ID: 14576837
3. Alderden et al., J. Chem. Ed. 2006, 83(5), 728-734.
|
Product Name: GSK1349572 (Dolutegravir) | HIV integrase inhibitor (#C4134-2s)
.png)
GSK1349572, a novel tricyclic-core containing inhibitor, has an IC50 of 2.7 nM against HIV-1 with a
corresponding EC50s of 0.51 nM, 0.71 nM, and 2.2 nM in PBMCs, MT-4 cells, and PHIV assays,
respectively. [1] Cytotoxic concentration (CC50) in unstimulated and stimulated PBMCs was 189 uM and 52
uM, which results in a selectivity index of 9400. Though similar in potency to first-generation integrase
inhibitors, Raltegravir and Elvitegravir, GSK1349572 possesses and resistance profile that is markedly
different. In cross-resistance profiling experiments, GSK1349572 showed efficacy against five non-
nucleoside- and nucleoside- reverse transcriptase inhibitor-resistant viruses equal to that of wild-type virus
(EC50 = 1.3 to 2.1 nM). Similarly, GSK1349572 was efficacious against two protease inhibitor-resistant
viruses, again equivalent to activity against wild-type virus (EC50 = 0.36 and 0.37 nM).
In studies of clinical isolates from HIV-2-infected patients, the median EC50 value for GSK1349572 was found
to be 0.8 nM. [2]
|
Details
|
Chemical Formula:
|
|
C20H19F2N3O5
|
|
CAS No.:
|
|
1051375-16-6
|
|
Molecular weight:
|
|
419.38
|
|
Purity:
|
|
> 98%
|
|
Appearance:
|
|
White
|
|
Chemical name:
|
|
2H-Pyrido[1',2':4,5]pyrazino[2,1-b][1,3]oxazine-9-carboxamide, N-[(2,4-
difluorophenyl)methyl]-3,4,6,8,12,12a-hexahydro-7-hydroxy-4-methyl-6,8-dioxo-,
(4R,12aS)
|
|
Solubility:
|
|
Up to 100 mM in DMSO
|
|
Synonyms:
|
|
GSK1349572, S/GSK1349572, Dolutegravir
|
|
Storage:
|
|
For longer shelf life, store solid powder at 4oC desiccated, or store DMSO solution
at -20oC
|
References
1. Kobayashi et al., In Vitro Antiretroviral Properties of S/GSK1349572, a Next-Generation HIV Integrase
Inhibitor. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 2011, 55(2), 813-821. Pubmed ID: 21115794
2. Charpentier et al., In vitro phenotypic susceptibility of HIV-2 clinical isolates to the integrase inhibitor
S/GSK1349572. AIDS, 2010, 24, 2753-2755. Pubmed ID: 20827161
|
Product Name: KU-55933 | ATM kinase inhibitor (#C5855-5)
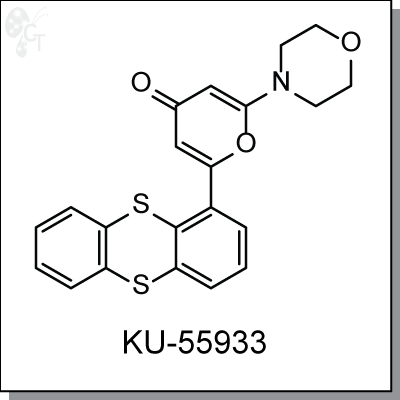
KU55933 is an ATP-competitive, thioanthrene-pyranone-based inhibitor of ATM kinase with an IC50 of 13 nM
and Ki of 2.2 nM and >100-fold selectivity over PI3K related kinases. [1] KU55933 inhibits cell proliferation by
inducing G1 cell cycle arrest by downregulation of cyclin D1 synthesis in MDA-MB-453 breast cancer cells
and PC-3 prostate cancer cells. [2] KU55933 inhibits insulin- and IGF1-stimulated Akt phosphorylation at both
Ser473 and Thr308. [2] ATM cellular inhibition by KU55933 was demonstrated in additional phosphorylation
targets, including p53 Ser15, H2AX Ser139, NBS1 Ser343, Chk1 Ser345, and SMC1 Ser966. [1]
KU55933 is being studied as a radiosensitizer, having been shown to sensitize HeLa cells to the effects of
topoisomerase inhibitors, etoposide, doxorubicin, amsacrine, and camptothecin. [1] When in combination
with rapamycin, KU55933 induces apoptosis and arrests any induced feedback activation of Akt. [2]
|
Details
|
Chemical Formula:
|
|
C21H17NO3S2
|
|
CAS No.:
|
|
587871-26-9
|
|
Molecular weight:
|
|
395.49
|
|
Purity:
|
|
> 98%
|
|
Appearance:
|
|
White
|
|
Chemical name:
|
|
2-morpholino-6-(thianthren-1-yl)-4H-pyran-4-one
|
|
Solubility:
|
|
Up to 100 mM in DMSO
|
|
Synonyms:
|
|
KU-55933, KU 55933, KU55933
|
|
Storage:
|
|
For longer shelf life, store solid powder at 4oC desiccated, or store DMSO solution
at -20oC
|
References
1. Hickson et al., Identification and characterization of a novel and specific inhibitor of the ataxia-
telangiectasia mutated kinase ATM. Cancer Res. 2004, 64(24), 9152-9159. Pubmed ID: 15604286
2. Li et al., The ATM inhibitor KU-55933 suppresses cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by blocking Akt
in cancer cells with overactivated Akt. Mol. Cancer. Ther. 2010, 9(1), 113-125. Pubmed ID: 20053781
|
Product Name: Temozolomide | DNA alkylating agent (#C8366-10)
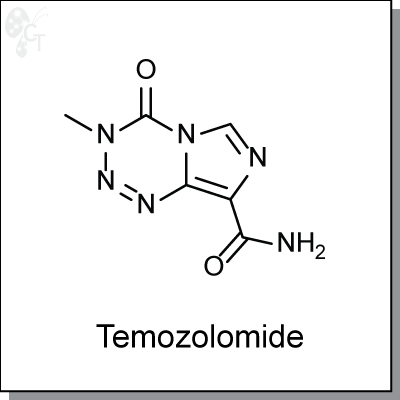
Temozolomide is an highly orally-available, imidazotetrazine-based, monofunctional DNA alkylating agent.
In vivo it spontaneously degrades and reacts with water to release a methyldiazonium cation which
preferentially methylates DNA at N7 positions of guanine in guanine rich regions. The active agent also
methylates N3 adenine and O6 guanine. [1]
Temozolomide, which enters the cerebrospinal fluid and does not require hepatic metabolism, demonstrates
schedule-dependent antitumor activity against highly-resistant gliomas. [2] In Phase 1 clinical studies,
temozolomide showed 100% p.o. bioavailability.
In L-1210 leukemia cells, temozolomide caused a dose-dependent accumulation of cells in the SL-G2-M
phase. [3]
|
Details
|
Chemical Formula:
|
|
C6H6N6O2
|
|
CAS No.:
|
|
85622-93-1
|
|
Molecular weight:
|
|
194.15
|
|
Purity:
|
|
> 99%
|
|
Appearance:
|
|
White
|
|
Chemical name:
|
|
4-methyl-5-oxo- 2,3,4,6,8-pentazabicyclo [4.3.0] nona-2,7,9-triene- 9-carboxamide
|
|
Solubility:
|
|
Up to 100 mM in DMSO
|
|
Synonyms:
|
|
Temozolomide, Temodar, Methazolastone
|
|
Storage:
|
|
For longer shelf life, store solid powder at 4oC desiccated, or store DMSO solution
at -20oC
|
References
1. Zhang et al., Temozolomide: mechanisms of action, repair and resistance. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2012, 5,
102-114. Pubmed ID: 22122467
2. Friedman et al., Temozolomide and treatment of malignant glioma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 2585-2597.
Pubmed ID: 10914698
3. Catapano et al., In vitro and in vivo methazolastone-induced DNA damage and repair in L-1210 leukemia
sensitive and resistant to chloroethylnitrosoureas. Cancer Res. 1987, 47, 4884-4889. Pubmed ID: 3621181
|
|

.png)

