Cellular Mechanism, Metabolism Synthesis / Degradation
Product Name: GW4064 l non-steroidal FXR agonist (#C4940-5)
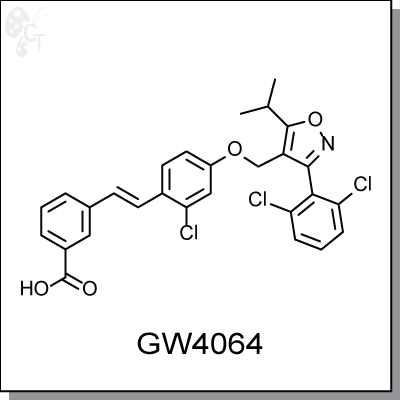
GW4064 is a potent, orally-available, non-steroidal, isoxazole-based agonist of FXR with an EC50 of 15 nM.
In a Fisher rat model, GW4064 was found to lower serum triglyceride levels in a dose-dependent manner and
an ED50 of 20 mg/kg. (1)
In C57BL/6 mice, GW4064 has been shown to stimulate plasma corticosterone levels, thus suggesting a role
in the modulation of adrenal cholesterol metabolism and glucocorticoid synthesis. (2)
Followup SAR studies have led to equipotent FXR analogs of GW4064 with improved developability
parameters, including reduced toxicity and cholestasis. (3)
|
Details
|
Chemical Formula:
|
|
C28H22Cl3NO4
|
|
CAS No.:
|
|
278779-30-9
|
|
Molecular weight:
|
|
542.84
|
|
Purity:
|
|
> 98%
|
|
Appearance:
|
|
White
|
|
Chemical name:
|
|
(E)-3-(2-chloro-4-((3-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-5-isopropylisoxazol-4-yl)methoxy)styryl)benzoic acid
|
|
Solubility:
|
|
Up to 100 mM in DMSO
|
|
Synonyms:
|
|
GW4064, GW-4064, GW 4064
|
|
Storage:
|
|
For longer shelf life, store solid powder at 4oC desiccated, or DMSO solution at -20oC
|
1. Maloney et al., Identification of a Chemical Tool for the Orphan Nuclear Receptor FXR. J. Med. Chem.
2000, 43(16), 2971-2974. Pubmed ID: 10956205
2. Hoekstra et al., FXR agonist GW4064 increases plasma glucocorticoid levels in C57BL/6 mice. Mol. Cell.
Endocrinol. 2012, 362, 69-75. Pubmed ID: 22643070
3. Akwabi-Ameyaw et al., Conformationally constrained farnesoid X receptor (FXR) agonists: Naphthoic
acid-based analogs of GW 4064. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 4339-4343. Pubmed ID: 18621523
|
Product Name: Lonidamine l Glycolysis inhibitor (#C5664-10)
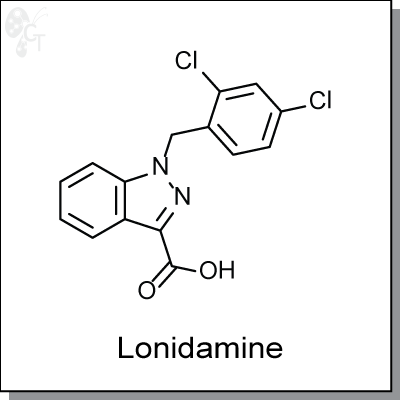
Lonidamine is an orally-available, indazole-based inhibitor of glycolysis by the inactivation of hexokinase.
Lonidamine is believed to increase apoptosis and in in vitro models has displayed markers of mitochondrial
membrane depolarization, cytochrome C release, phosphatidylserine externalization, and DNA
fragmentation. In support of apotosis induction, caspase activity was found to be enhanced by Lonidamine in
LNCaP cells. (1)
In separate studies, lonidamine was found to act of mitochondra to induce apoptosis by dissipating the inner
transmembrane potential and the release of key apoptotic factors. (2)
|
Details
|
Chemical Formula:
|
|
C15H10Cl2N2O2
|
|
CAS No.:
|
|
50264-69-2
|
|
Molecular weight:
|
|
321.16
|
|
Purity:
|
|
> 98%
|
|
Appearance:
|
|
white
|
|
Chemical name:
|
|
1-(2,4-dichlorobenzyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxylic acid
|
|
Solubility:
|
|
Up to 100 mM in DMSO
|
|
Synonyms:
|
|
0
|
|
Storage:
|
|
For longer shelf life, store solid powder at 4oC desiccated, or DMSO solution at -20oC
|
References
1. Brawer et al., Lonidamine: Basic Science and Rationale for Treatment of Prostatic Proliferative Disorders.
Rev. Urol. 2005, 7, suppl. 7, S21-S26. Pubmed ID: 16986057
2. Ravagnan et al., Lonidamine triggers apoptosis via a direct, Bcl-2-inhibited effect on the mitochondrial
permeability transition pore. Oncogene, 1999, 18, 2537-2546. Pubmed ID: 10353597
|
Product Name: Ormetoprim |Dihydrofolate (DHF) reductase (#C6763-10)
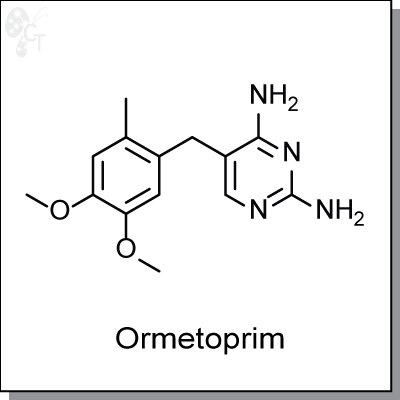
Ormetoprim is a diaminopyrimidine-based inhibitor of dihydrofolate reductase, the enzyme responsible for
NADPH-dependent reduction of 7,8-dihydrofolate to 5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate. (1) This inhibition results in the
interference in folic acid production. In bacteria, Ormetoprim, weakly antibacterial by itself, can act as a
potentiator by cotreatment with sulfadimethoxine, which in turn prevents the formation of folinic acid. (2)
|
Details
|
Chemical Formula:
|
|
C14H18N4O2
|
|
CAS No.:
|
|
6981-18-6
|
|
Molecular weight:
|
|
274.32
|
|
Purity:
|
|
> 98%
|
|
Appearance:
|
|
white
|
|
Chemical name:
|
|
2,4-Diamino-5-(6-methylveratryl)pyrimidine
|
|
Solubility:
|
|
Up to 100 mM in DMSO
|
|
Synonyms:
|
|
0
|
|
Storage:
|
|
For longer shelf life, store solid powder at 4oC desiccated, or DMSO solution at -20oC
|
References
1. Manchand et al., Syntheses of Antibacterial 2,4-Diamino-5 benzylpyrimidines. Ormetoprim and
Trimethoprim. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 3531-3535.
2. Boothe, D.M., Sulfonamides and Sulfonamide Combinations, Merck Manuals, March, 2012.
|
Product Name: PF-3845 | FAAH inhibitor (#C7384-5)
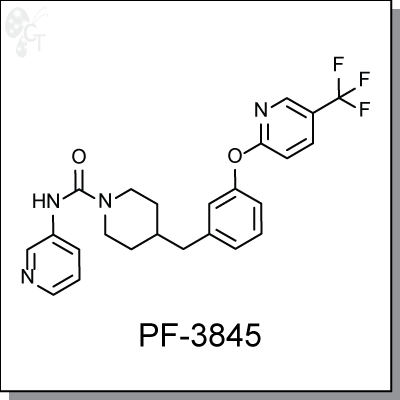
PF-3845 is an orally-available, covalent and irreversible inhibitor of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) for the
treatment of inflammation and pain, with an IC50 of 7.2 nM. [1] Mechanistic studies show that PF-3845 is a
time-dependent inhibitor that carbamylates FAAH's catalytic serine nucleophile and raises anandamide
levels in the brain for up to 24h. [2, 3]
Oral administration of PF-3845 produces antinociceptive effects in both inflammatory and noninflammatory
pain models in rats with an MED 0.1 mg/kg. [2] Furthermore, oral administration of PF-3845 at 0.1 mg/kg
results in efficacy comparable to that of naproxen at 10 mg/kg in a rat inflammatory pain model. [1]
Regarding the encannabinoid system, PF-3845 has been shown to be an effective treatment (i.p.) for the
blockade of neuronal FAAH to reverse allodynia through the activation of both cannabinoid receptors,
without the psychomimetic side effects associated with THC. [4]
|
Details
|
Chemical Formula:
|
|
C24H23F3N4O2
|
|
CAS No.:
|
|
1196109-52-0
|
|
Molecular weight:
|
|
456.46
|
|
Purity:
|
|
> 98%
|
|
Appearance:
|
|
white
|
|
Chemical name:
|
|
4-(3-(5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-yloxy)benzyl)-N-(pyridin-3-yl)piperidine-1-carboxamide
|
|
Solubility:
|
|
Up to 100 mM in DMSO
|
|
Synonyms:
|
|
PF-3845, PF 3845, PF3845
|
|
Storage:
|
|
For longer shelf life, store solid powder at 4oC desiccated, or DMSO solution at -20oC
|
References
1. Johnson et al., Discovery of PF-04457845: A Highly Potent, Orally Bioavailable, and Selective Urea FAAH
Inhibitor. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 91-96. Pubmed ID: 21666860
2. Ahn et al., Mechanistic and pharmacological characterization of PF-04457845: a highly potent and selective
fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor that reduces inflammatory and noninflammatory pain. J. Pharmcol.
Exp. Ther. 2011, 338 (1), 114-124. Pubmed ID: 21505060
3. Ahn et al., Discovery and characterization of a highly selective FAAH inhibitor that reduces inflammatory
pain. Chem. Biol. 2009, 16(4), 411-420. Pubmed ID: 19389627
4. Booker et al., The fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) inhibitor PF-3845 acts in the nervous system to
reverse LPS-induced tactile allodynia in mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165(8), 2485-2496. Pubmed ID:
21505060
|
|



