UCH-L1 inhibitor & other new products of Cellagen Tech.
본문
UCH-L1 inhibitor & other new products of Cellagen Technology
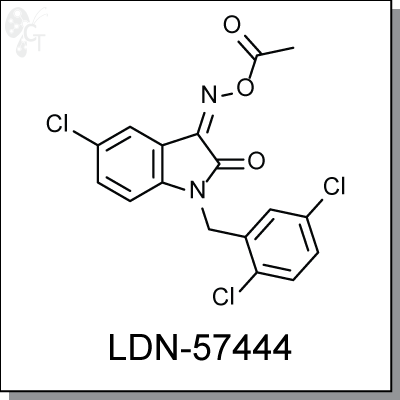
Product Name: LDN-57444 | UCH-L1inhibitor (#C5574)
|
LDN-57444 is a specific inhibitor (Ki = 0.4 ?M) against Ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCH-L1), a member of deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs). LDN-57444 increased proliferation of SH-SY5Y cells, a UCH- L1-expressing neuroblastoma line. [1]
As expression of UCH-L1 is highly specific to neurons and to cells of the diffuse neuroendocrine system and their tumors, LDN-57444 is a useful tool for studying the roles of UCH-L1 in Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and other neurological disorders. [2,3] |
Details
|
Chemical Formula: |
|
C17H11Cl3N2O3 |
|
CAS No.: |
|
668467-91-2 |
|
Molecular weight: |
|
397.64 |
|
Purity: |
|
> 98% |
|
Appearance: |
|
Yellow |
|
Chemical name: |
|
1H-Indole-2,3-dione, 5-chloro-1-[(2,5-dichlorophenyl)methyl]-, 3-(O-acetyloxime) |
|
Solubility: |
|
Up to 25 mM in DMSO |
|
Synonyms: |
|
LDN-57444, LDN57444 |
|
Storage: |
|
For longer shelf life, store solid powder or DMSO solution at -20oC |
|
References 1. Liu Y, et al. Discovery of inhibitors that elucidate the role of UCH-L1 activity in the H1299 lung cancer cell line. Chem Biol. 2003; 10(9):837-46. Pubmed ID: 14522054 2. Cartier AE, et al. Regulation of synaptic structure by ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1. J Neurosci. 2009; 29 (24):7857-68. Pubmed ID: 19535597 3. Zhang M, et al. Control of BACE1 degradation and APP processing by ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase L1. J Neurochem. 2012; 120(6):1129-38. Pubmed ID: 22212137 |
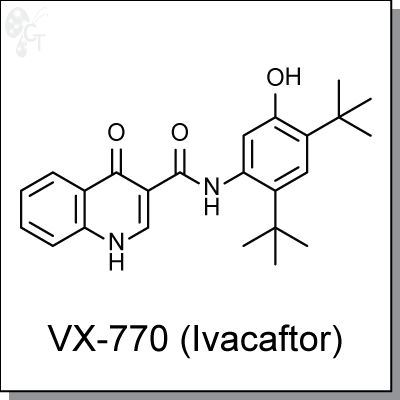
Product Name: VX-770 (Ivacaftor) | CFTR potentiator (#C8770)
|
VX-770 (Ivacaftor) is a CFTR potentiator and has been shown to potentiate normal CFTR, as well as CFTR with G551D and F508-del mutations. Ivacaftor directly binds to the ion channel, causes conformation change and open the ion channel to improve chloride transportation. In primary cultured human CF bronchial epithelia (HBE) carrying the G551D and F508del CFTR mutations, Ivacaftor (10 ?M) potently increases the forskolin- stimulated Cl- secretion with an EC50 of 236 nM. [1]
VX-770 (Ivacaftor) is approved for cystic fibrosis patients with G551D mutation, and has shown efficacy in a patient with S549N mutation. [2] |
Details
|
Chemical Formula: |
|
C24H28N2O3 |
|
CAS No.: |
|
873054-44-5 |
|
Molecular weight: |
|
392.49 |
|
Purity: |
|
> 98% |
|
Appearance: |
|
Off-white |
|
Chemical name: |
|
N-(2,4-di-tert-butyl-5-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxamide |
|
Solubility: |
|
Up to 100 mM in DMSO |
|
Storage: |
|
For longer shelf life, store solid powder or DMSO solution at -20oC |
| References 1. Van Goor F et al. Rescue of CF airway epithelial cell function in vitro by a CFTR potentiator, VX-770. , Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009; 106(44):18825-30. Pubmed ID: 19846789 2. McGarry ME and Nielson DW. Normalization of sweat chloride concentration and clinical improvement with ivacaftor in a patient with cystic fibrosis with mutation S549N. Chest. 2013; 144(4):1376-8. Pubmed ID: 24081349 |
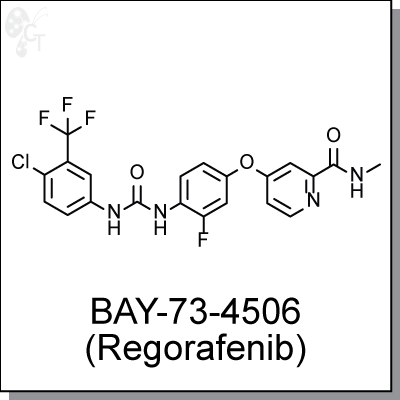
Product Name: BAY-73-4506 (Regorafenib) | Tyrosine kinase inhibitor (#C2734)
|
BAY-73-4506 (Regorafenib) is an orally active and highly potent inhibitor against multiple tyrosine kinases, including VEGFR1/2/3, PDGFR?, Kit, RET and Raf-1. Regorafenib inhibits the proliferation of HUVEC cells stimulated with VEGF, and inhibits FGFR signaling in breast cancer MCF-7 cells stimulated with FGF. Regorafenib is anti-angiogenic due to its inhibitions against VEGFR2-TIE2 tyrosine kinase. [1] Co-administration of Regorafenib and a PI3K/Akt inhibitor (MK-2206) clearly demonstrated synergistic effect in a HCT116 xenocraft mouse model [2]. Regorafenib is currently being studied as a potential treatment option in multiple tumor types, and has recently be approved in treating patients with Metastatic Colorectal cancer. [3] |
Details
|
Chemical Formula: |
|
C21H15CIF4N4O3 |
|
CAS No.: |
|
755037-03-7 |
|
Molecular weight: |
|
482.82 |
|
Purity: |
|
> 98% |
|
Appearance: |
|
White |
|
Chemical name: |
|
1-(4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-3-(2-fluoro-4-(2-(methylcarbamoyl)pyridin- 4-yloxy)phenyl)urea |
|
Solubility: |
|
Up to 100 mM in DMSO |
|
Synonyms: |
|
BAY-73-4506, BAY73-4506, Regorafenib, Fluoro-Sorafenib |
|
Storage: |
|
For longer shelf life, store solid powder or DMSO solution at -20oC |
|
References 1. Wilhelm SM et al, Regorafenib (BAY 73-4506): a new oral multi-kinase inhibitor of angiogenic, stromal and oncogenic receptor tyrosine kinases with potent preclinical antitumor activity. Int J Cancer. 2011; 129:245-55 Pubmed ID: 21170960 2. Sajithlal GB et al. Sorafenib/regorafenib and phosphatidyl inositol 3 kinase/thymoma viral proto-oncogene Inhibition interact to kill tumor cells. Mol Pharmacol. 2013; 84(4):562-71. Pubmed ID: 23877009 3. Carter NJ. Regorafenib: a review of its use in previously treated patients with progressive metastatic colorectal cancer. Drugs Aging. 2014; 31(1):67-78. Pubmed ID: 24276917 |
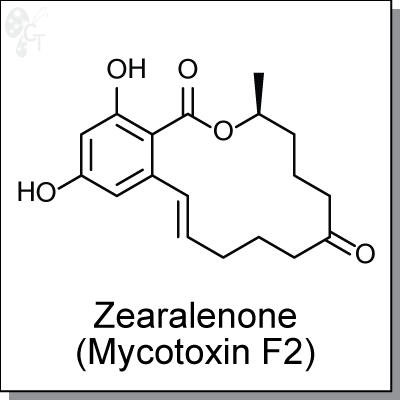
Product Name: Zearalenone (Toxin F2) | ER agonist (#C9327)
|
Zearalenone is a heat-resistant mycotoxin produced by fungi in food and animal feeds [1]. It acts as an estrogen receptor agonist and can cause hormonal effects in animal species such as the pig [2]. Evidence for Zearalenone effects have been observed in a wide variety of animals. The association between Zearalenone exposure and human diseases remains speculative at present; it has been considered as a possible causative agent in outbreaks of precocious pubertal changes in young children and has been suggested to have a possible involvement in human cervical cancer. [3,4] |
Details
|
Chemical Formula: |
|
C18H22O5 |
|
CAS No.: |
|
17924-93-4 |
|
Molecular weight: |
|
318.36 |
|
Purity: |
|
> 98% |
|
Appearance: |
|
Off-white |
|
Chemical name: |
|
(3S,?11E)-?3,?4,?5,?6,?9,?10-?hexahydro-?14,?16-?dihydroxy-?3-?methyl-?1H-?2- ?benzoxacyclotetradecin-?1,?7(8H)-?dione |
|
Solubility: |
|
Up to 50 mM in DMSO |
|
Synonyms |
|
Zearalenone, Mycotoxin F2, FES, Zenone, Toxin F2 |
|
Storage: |
|
For longer shelf life, store solid powder or DMSO solution at -20oC |
|
References: 1. Zinedine A, et al. Review on the toxicity, occurrence, metabolism, detoxification, regulations and intake of zearalenone: An oestrogenic mycotoxin. Food Chem Toxicol, 2007; 45:1-18 Pubmed ID: 17045381 2. Tiemann U. and Dänicke S. In vivo and in vitro effects of the mycotoxins zearalenone and deoxynivalenol on different non-reproductive and reproductive organs in female pigs: A review.Food Addit Contam, 2007; 24:306-314 Pubmed ID: 17364934 3. Caloni F. and Cortinovis C. Effects of fusariotoxins in the equine species. Vet J, 2010; 186:157-161 Pubmed ID: 19837621 4. Massart F. and Saggese G. Oestrogenic mycotoxin exposures and precocious pubertal development. Int J Androl, 2010; 33:369-376 Pubmed ID: 17364934 |
Product Name: NVP-LGK974 | Wnt inhibitor (#C6545)
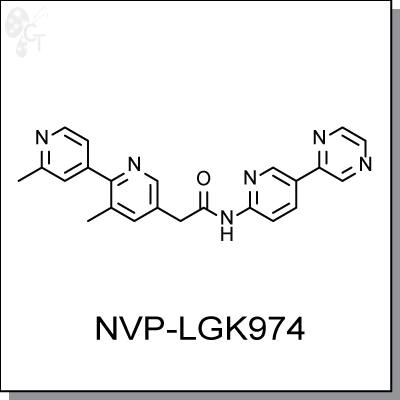
|
LGK974 is a potent and orally active Wnt pathway inhibitor with an IC50<1 nM in the Wnt signaling assay [1]. It inhibits acylation of Wnt proteins by Porcupine (Porcn). LGK974 specifically blocks the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells that have up-regulated Wnt signaling caused by carrying inactive mutations in a Ubiquitin E3 ligase, RNF43 [2].
LGK974 robustly suppressed Wnt signaling in vivo resulting in tumor regression in a murine breast cancer model driven by MMTV-Wnt1, and showed excellent efficacy in xenograft models of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and pancreatic cancer [3]. Currently LGK974 is in the Phase I study to treat patients with different types of Wnt signaling-driven cancers [4]. |
Details
|
Chemical Formula: |
|
C23H20N6O |
|
CAS No.: |
|
1243244-14-5 |
|
Molecular weight: |
|
396.44 |
|
Purity: |
|
> 98% |
|
Appearance: |
|
White |
|
Chemical name: |
|
2-(2',3-dimethyl-[2,4'-bipyridin]-5-yl)-N-(5-(pyrazin-2-yl)pyridin-2-yl)acetamide |
|
Solubility: |
|
Up to 100 mM in DMSO |
|
Synonyms: |
|
NVP-LGK974, LGK974 |
|
Storage: |
|
For longer shelf life, store solid powder or DMSO solution at -20oC |
|
References: 1. Shifeng Pan. Discovery of LGK974: A selective Porcupine inhibitor targeting Wnt signaling in cancer. AACR Annual Meeting 2013. 2. Jiang X, et al. Inactivating mutations of RNF43 confer Wnt dependency in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013; 110(31):12649-54. Pubmed ID: 23847203 3. Liu J, et al. Targeting Wnt-driven cancer through the inhibition of Porcupine by LGK974. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013; 110(50):20224-9 Pubmed ID: 24277854 |
Ordering informations
|
Catalog No. |
Product Name |
Size |
|
C5574 |
LDN-57444 | UCH-L1inhibitor |
5mg, 25mg & 100mg |
|
C8770 |
VX-770 (Ivacaftor) | CFTR potentiator |
5mg, 25mg & 100mg |
|
C2734 |
BAY-73-4506 (Regorafenib) | Tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
5mg, 25mg & 100mg |
|
C9327 |
Zearalenone (Toxin F2) | ER agonist |
10mg, 50mg & 250mg |
|
C6545 |
NVP-LGK974 | Wnt inhibitor |
2mg, 10mg & 50mg |
* 관련제품 정보
Stem Cell Pathway and Chemical Modulators
Stem Cell Pathway Modulating Compounds
▣ 관련 페이지 ; Cellangen Technology
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.