Cellular Mechanism, Apoptosis I
Product Name: ABT-263 (Navitoclax) | Bcl-2 family inhibitor (#C2263)
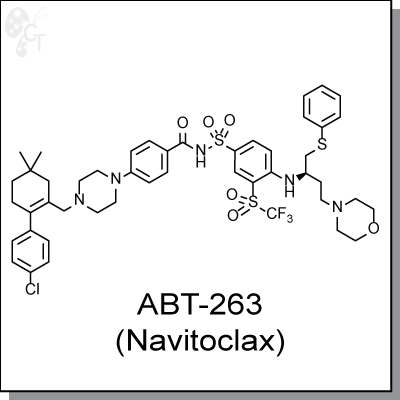
ABT-263 is an orally-available Bcl-2 family inhibitor with Ki values of < 1 nM for Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, and Bcl-w.
ABT-263 disrupts key Bcl interactions with proteins such as Bim, inducing apoptosis. Despite being a Bad-
like Bh3 mimetic, ABT-263 has been shown to possess cytotoxic activity and induce apoptosis based
primarily on its Bcl-2 family inhibitory activity.
ABT-263 as a standalone agent has modest activity in lymphoma and myeloma xenografts, but is extremely
effective in enhancing the efficacy of clinically relevant therapies such as rituxumab and bortezomib. (1)
In a panel of small cell lung cancer (SCLC) xenografts, including H146, H889, and H1963 models, ABT-263
displays excellent antitumor effects, leading to tumor regression. (2)
|
Details
|
Chemical Formula:
|
|
C47H55CIF3N5O6S3
|
|
CAS No.:
|
|
923654-51-6
|
|
Molecular weight:
|
|
974.61
|
|
Purity:
|
|
> 98%
|
|
Appearance:
|
|
White
|
|
Chemical name:
|
|
(R)-4-(4-((4'-chloro-4,4-dimethyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-[1,1'-biphenyl]-2-yl)methyl)
piperazin-1-yl)-N-((4-((4-morpholino-1-(phenylthio)butan-2-yl)amino)-3-
((trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)benzamide
|
|
Solubility:
|
|
Up to 100 mM in DMSO
|
|
Synonyms:
|
|
ABT-263, Navitoclax, ABT263, ABT 263
|
|
Storage:
|
|
For longer shelf life, store solid powder or DMSO solution at -20oC
|
1. Tse et al., ABT-263: A Potent and Orally Bioavailable Bcl-2 Family Inhibitor. Cancer Res. 2008, 68,
3421-3428. Pubmed ID: 18451170
2. Shoemaker et al., Activity of the Bcl-2 Family Inhibitor ABT-263 in a Panel of Small Cell Lung Cancer
Xenograft Models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 3268-3277. Pubmed ID: 18519752
|
Product Name: ABT-737 | Apoptosis inhibitor (#C2281)
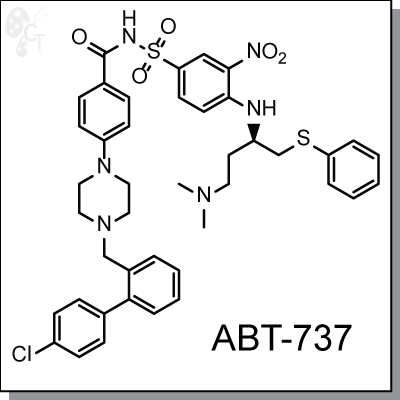
ABT-737 is a selective and potent small molecule inhibitor of protein Bcl-2, Bcl-XL, and Bcl-w. Like a BAD
BH3 peptide, ABT-737 binds to and antagonizes anti-apototic Bcl-2 family proteins instead of directly
activating the apoptotic process. ABT-737 binds with high affinity (ki < 1nm) to Bcl-XL, Bcl-2 and Bcl-w, but
not to Bcl-B, Mcl-1 and Al protein.
ABT-737 displays a wide range of single-agent activity against cells from lymphoma, leukemia, solid tumor
SCLC, and primary cells derived from patient. In animal models, ABT-737 causes tumor regression and
improves survival1-2. ABT-737 has shown synergistic anti-tumor activity when used together with vorinostat
or bemicitabine3,4.
|
Details
|
Chemical Formula:
|
|
C42H45CIN6O5S2
|
|
CAS No.:
|
|
852808-04-9
|
|
Molecular weight:
|
|
813.43
|
|
Purity:
|
|
> 98%
|
|
Appearance:
|
|
Off white solid
|
|
Chemical name:
|
|
4-[4-[(4'-Chloro[1,1'-biphenyl]-2-yl)methyl]-1-piperazinyl]-N-[[4-[[(1R)-3-
(dimethylamino)
-1-[(phenylthio)methyl]propyl]amino]-3-nitrophenyl]sulfonyl]benzamide
|
|
Solubility:
|
|
Up to 50 mM in DMSO
|
|
Storage:
|
|
For longer shelf life, store solid powder or DMSO solution at -20oC
|
References
1. Oltersdorf, T. et al. An inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins induces regression of solid tumours. Nature. 2005
Jun 2;435(7042):677-81.
2. Van Deelft , MF. et al. The BH3 mimetic ABT-737 targets selective Bcl-2 proteins and efficiently induces
apoptosis via Bak/Bax if Mcl-1 is neutralized. Cancer Cell. 2006 Nov;10(5):389-99.
3. Zhang, C. et al. Synergistic anti-tumor activity of gemcitabine and ABT-737 in vitro and in vivo through
disrupting the interaction of USP9X and Mcl-1. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011 Jul;10(7):1264-75.
4. Wiegmans AP, et al. Deciphering the molecular events necessary for synergistic tumor cell apoptosis
mediated by the histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat and the BH3 mimetic ABT-737. Cancer Res. 2011
|
Product Name: BSI-201 (Iniparib) | PARP inhibitor (#C2201)
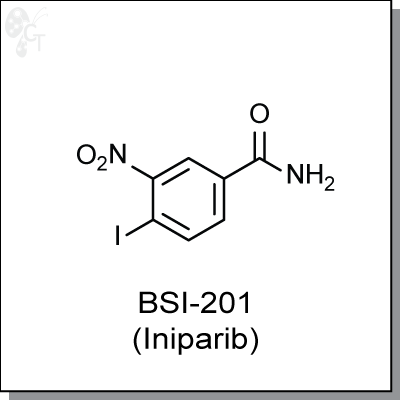
BSI-201 (Iniparib), a iodonitrobenzamide-based cytotoxic agent, was initially considered to be a PARP
inhibitor based on its abillity to inactivate PARP by means of zinc ejection from the zinc finger of the enzyme.
[1]
Despite its ability to kill normal and neoplastic cells at high concentrations (>40 uM), further studies revealed
that BSI-201 did not selectivly kill homologous-recombination (HR)-deficient cells, sensitize cells to
topoisomerase I poisons, or inhibit PARP in situ, as seen with olaparib and veliparib. [2]
Through a battery of enzymatic, cellular, and viability assays, BSI-201 was shown to nonselectively modify
cysteine-containing proteins in tumor cells. It is also postulated that the formation of nonspecific adducts can
alter stability, activity, and localization, thus inducing apoptosis, stress, cell-cycle perturbation, or DNA
damage. [3]
|
Details
|
Chemical Formula:
|
|
C7H5IN2O3
|
|
CAS No.:
|
|
160003-66-7
|
|
Molecular weight:
|
|
292.03
|
|
Purity:
|
|
> 98%
|
|
Appearance:
|
|
White
|
|
Chemical name:
|
|
4-iodo-3-nitrobenzamide
|
|
Solubility:
|
|
Up to 100 mM in DMSO
|
|
Synonyms:
|
|
BSI-201, BSI201, BSI 201, 160003-66-7, Iniparib
|
|
Storage:
|
|
For longer shelf life, store solid powder or DMSO solution at -20oC
|
References
1. Mendeleyev et al., Potential chemotherapeutic activity of 4-iodo-3-nitrobenzamide. Biochem. Pharmacol.
1995, 50(5), 705-714. Pubmed ID: 7669074
2. Patel et al., Failure of Iniparib to inhibit poly(ADP-Ribose) polymerase in vitro. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18,
1655-1662. Pubmed ID: 22291137
3. Liu et al., Iniparib nonselectively modifies cysteine-containing proteins in tumor cells and is not a bonafide
PARP inhibitor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 510-523.
|
Product Name: CDDO (Bardoxolone) | anti-inflammatory (#C2336)
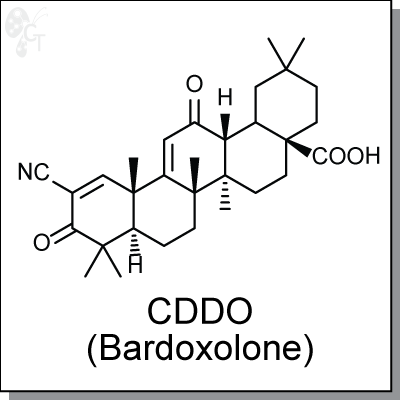
CDDO is a synthetic oleanane triterpenoid. It is 400,000x more potent than natural product oleanolic acid in
inhibiting cellular iNOS production when stimulated by IFN-gamma, TNF-alpha, and IL-1 [1]. The
mechanism of action of CDDO remain elusive, despite its broad biological activities, including proliferation
inhibition, apoptosis induction[2], and oxidative stress and inflammation suppression.
CDDO-methyl ester,an orally-available form of CDDO, is undergoing clinical development for the treatment of
advanced chronic kidney disease (CKD) in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.
|
Details
|
Chemical Formula:
|
|
C31H41NO4
|
|
CAS No.:
|
|
218600-44-3
|
|
Molecular weight:
|
|
491.66
|
|
Purity:
|
|
> 98%
|
|
Appearance:
|
|
Brown
|
|
Chemical name:
|
|
2-cyano-3,12-dioxo-oleana-1,9(11)-dien-28-oic acid
|
|
Solubility:
|
|
Up to 10 mM in DMSO
|
|
Synonyms:
|
|
CDDO, RTA-401, RTA401, Bardoxolone
|
|
Storage:
|
|
For longer shelf life, store solid powder or DMSO solution at -20oC
|
References
1. Sporn MB, et al. New synthetic triterpenoids: potent agents for prevention and treatment of tissue injury
caused by inflammatory and oxidative stress. J Nat Prod. 2011; 74(3):537-45. Pubmed ID: 21309592
2. Suh N, et al. A novel synthetic oleanane triterpenoid, 2-cyano-3,12-dioxoolean-1,9-dien-28-oic acid, with
potent differentiating, antiproliferative, and anti-inflammatory activity. Cancer Res. 1999; 59(2):336-41.
Pubmed ID: 9927043
|
Product Name: Necrostatin-1 | RIP1 inhibitor (#C6221)
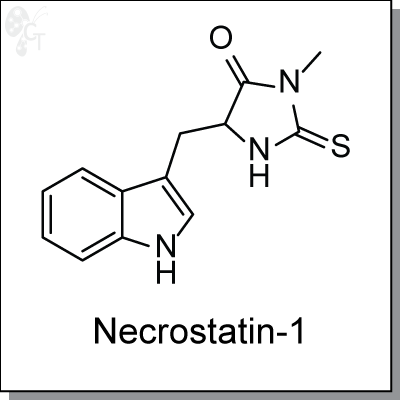
Necrostatin-1 is a specific ATP-competitive allosteric inhibitor (EC50 = 180 nM) of death domain receptor-
associated adaptor kinase (RIP1)1. It selectively blocks a specific programmed cell death pathway,
necroptosis, which leads to necrosis. While affecting this distinct cell death pathway, Necrostatin-1 does not
present any perturbation of the Fas/TNFR triggered canonical apoptosis cascade. Necrostatin-1 inhibits the
necrosis-induced RIP1 and RIP3 interactions in vitro2and reduces ischemic brain injury in a mouse model of
stroke3.
|
Details
|
Chemical Formula:
|
|
C13H13N13OS
|
|
CAS No.:
|
|
4311-88-0
|
|
Molecular weight:
|
|
259.33
|
|
Purity:
|
|
> 98%
|
|
Appearance:
|
|
Light yellow solid
|
|
Chemical name:
|
|
5-((1H-indol-3-yl)methyl)-3-methyl-2-thioxoimidazolidin-4-one
|
|
Solubility:
|
|
Up to 50 mM in DMSO
|
|
Storage:
|
|
For longer shelf life, store solid powder or DMSO solution at -20oC
|
References
1. Degterev A., et al. Identification of RIP1 kinase as a specific cellular target of necrostatins. Nat. Chem. Biol.
(2008), 4:313-321
2. Sun L., et al. Mixed Lineage Kinase Domain-like Protein Mediates Necrosis Signaling Downstream of RIP3
Kinase. Cell (2012), 148:213-227.
3. Degterev A., et al. Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain
injury. Nat. Chem. Biol. (2005), 1:112-119
|
|




