Cellular Mechanism, Metabolism_DNA/RNA synthesis I
Product Name: ABT-888 (Veliparib) l PARP1/2 inhibitor (#C2888)
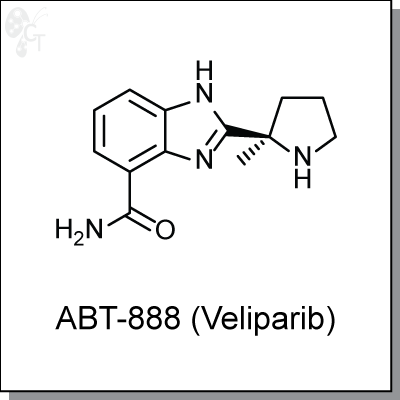
ABT-888 (Veliparib) is an orally-available, benzimidazole-based inhibitor of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase
with Ki values of 5.2 and 2.9 nM, for PARP1 and PARP2, respectively. [1] ABT-888 exhibits activity in C41
whole cells at an EC50 of 2 nM [2], and inhibits PAR formation in cells at an EC50 of 4.5 nM. [3]
ABT-888 efficiently crosses the blood-brain barrier and has been shown to potentiate DNA-damaging agents
such as temozolomide, cisplatin, carboplatin, cyclophosphamide, irinotecan, and radiation. [1, 4] Treatment
with temozolomide in the S phase generated higher levels of double-stranded DNA breaks and general
higher levels of cytoxicity.
|
Details
|
Chemical Formula:
|
|
C13H16N4O
|
|
CAS No.:
|
|
912444-00-9,912445-05-7
|
|
Molecular weight:
|
|
244.29
|
|
Purity:
|
|
> 98%
|
|
Appearance:
|
|
White solid
|
|
Chemical name:
|
|
(R)-2-(2-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-4-carboxamide
|
|
Solubility:
|
|
Up to 75 mM in DMSO
|
|
Synonyms:
|
|
ABT-888, ABT 888, ABT888, Veliparib
|
|
Storage:
|
|
For longer shelf life, store solid powder at 4oC desiccated, or DMSO solution at -20oC
|
1 Palma et al., The PARP inhibitor, ABT-888 potentiates temozolomide: correlation with drug levels and
reduction in PARP activity in vivo. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 2625-2636. Pubmed ID: 19035287
2. Penning et al., Discovery of the Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor 2-[(R)-2-methylpyrrolidin-
2-yl]-1H-benzimidazole-4-carboxamide (ABT-888) for the treatment of cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52,
514-523. Pubmed ID: 19143569
3. Liu et al., Potentiation of temozolomide cytotoxicity by poly(ADP)ribose polymerase inhibitor ABT-888
requires a conversion of single-stranded DNA damages to double-stranded DNA breaks. Mol. Cancer Res.
2008, 6, 1621-1629. Pubmed ID: 18922977
4. Donawho et al., ABT-888, an orally active poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor that potentiates DNA-
damaging agents in preclinical tumor models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13(9), 2728-2737.
Pubmed ID: 19143569
|
Product Name: Adriamycin (Doxorubicin) l DNA intercalator (#C2374)
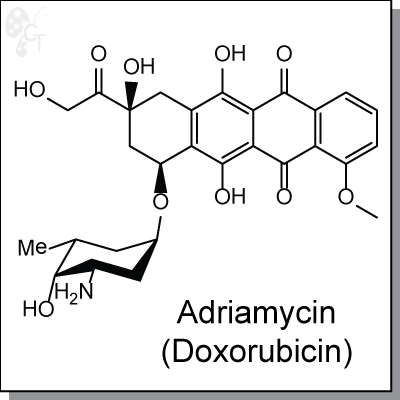
Adriamycin (Doxorubicin) is an intravenous, anthracycline-based antibiotic and antineoplastic agent derived
from Streptomyces bacterium. Adriamycin enters cancer cell DNA and inhibits cell replication by arresting
protein synthesis.
In HK-2 cells, adriamycin decreases cell viability in a dose-dependent manner and induces an increase in
cells in the sub G1 and G2/M phases. It also increases secretion of TNFa, decreases expression of
phosphorylated PKA and Bcl-2, and increases phosphoryled signal transducer and activator of transcription
3, phospho-ERK,and ATF3. [1]
Due to adriamycin's route of administration and cytotoxic effects, extensive research has been conducted in
the area of assisted delivery of the chemotherapeutic (liposome [2], prodrug [3], polymer, gold-particles,
etc.)
|
Details
|
Chemical Formula:
|
|
C27H29NO11HCl
|
|
CAS No.:
|
|
25316-40-9
|
|
Molecular weight:
|
|
579.98
|
|
Purity:
|
|
> 98%
|
|
Appearance:
|
|
Red Orange
|
|
Chemical name:
|
|
(8S,10S)-10-((2R,4S,5S,6S)-4-amino-5-hydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yloxy)-6,8,11-trihydroxy-8-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-1-methoxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrotetracene-5,12-dione hydrochloride
|
|
Solubility:
|
|
Up to 100 mM in DMSO
|
|
Storage:
|
|
For longer shelf life, store solid powder at 4oC desiccated, or DMSO solution at -20oC
|
References
1. Park et al., Doxorubicin induces cytotoxicity through upregulation of pERK-dependent ATF3. PLoSONE,
2012, 7(9), e44990. Pubmed ID: 23028726
2. Macmillan and Cancer Backup factsheet
3. Albright et al., Matrix metalloproteinase-activated doxorubicin prodrugs inhibit HT1080 xenograft growth
better than doxorubicin with less toxicity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2005, 4, 751-760. Pubmed ID: 15897239
|
Product Name: AG-014699 (PF-01367338, Rucaparib) | PARP1/2 inhibitor (#C2401)
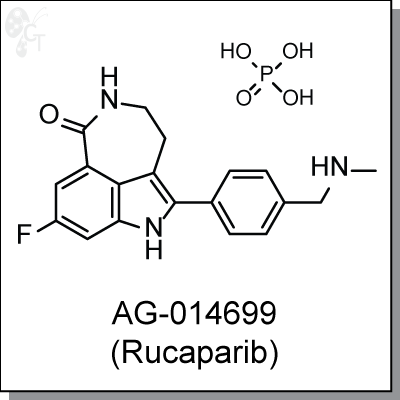
AG-014699 (Rucaparib) is an intraveneously-administered, azepinone-indole-based inhibitor of PARP 1 and 2
(Ki = 1.4 nM) [1] AG-014699 induces selective cytotoxicity in tumor cells defective in homologous
recombination repair (HRR) through BRCA1 and 2 mutation and non-BRCA mutated HRR defects. It is a potent
chemosensitizer of temozolomide (3 to 10 fold) and topotecan (1.5 to 2.3 fold) antitumor activity in
neuroblastoma cells. [2, 3]
|
Details
|
Chemical Formula:
|
|
C19H18FN3O.H3PO4
|
|
CAS No.:
|
|
459868-92-9
|
|
Molecular weight:
|
|
421.36
|
|
Purity:
|
|
> 98%
|
|
Appearance:
|
|
Yellow
|
|
Chemical name:
|
|
8-Fluoro-2-(4-methylaminomethyl-phenyl)-1,3,4,5-tetrahydro-azepino[5,4,3-cd]indol-6-one phosphate
|
|
Solubility:
|
|
Up to 100 mM in DMSO
|
|
Synonyms:
|
|
AG-014699, AG014699, AG-14699, AG-014447, PF-01367338, PF01367338,
Rucaparib phosphate, Rucaparib
|
|
Storage:
|
|
For longer shelf life, store solid powder at 4oC desiccated, or DMSO solution at -20oC
|
References
1. "Phase II trial of the Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor AG-014699 in BRCA1 and 2 mutated
advanced ovarian and breast cancer" Cancer Research UK / Newcastle Univ. Abstract 3104
2. Thomas et al., Preclinical selection of a novel poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor for clinical trial. Mol.
Cancer. Ther. 2007, 6(3), 945-956. Pubmed ID: 17363489
3. Daniel et al., Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 enhances temozolomide and topotecan activity
against childhood neuroblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15(4), 1241-1249. Pubmed ID: 19174487
|
Product Name: AZD2281 (Olaparib) | PARP1/2 inhibitor (#C2228)
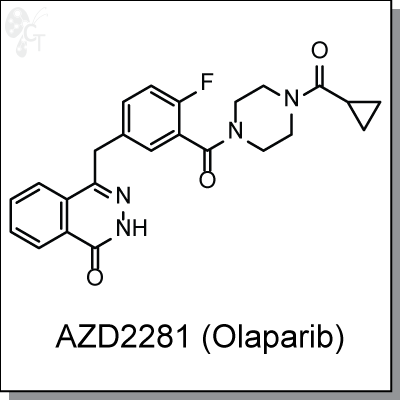
AZD2281 (olaparib) is phthalazinone-based PARP inhibitor with a potencies of 5 nM and 1 nM for PARP1 and
PARP2, respectively. It has been shown to be efficacious in the treatment of breast cancer tumors with BRCA
mutations. Specifically, BRCA2 deficient tumor cells showed the strongest differential growth inhibition upon
treatment with AZD2281 when compared to BRCA2-proficient cells. [1]
AZD2281 has been studied in combination therapies with platinum-based drugs and taxanes; specifically,
synergistic toxicity in BRCA2-deficient cells has been shown with cisplatin. [1] AZD2281 has been shown to
be a radiosensitizer in the treatment of NSCLC cells. [2]
|
Details
|
Chemical Formula:
|
|
C24H23FN4O3
|
|
CAS No.:
|
|
763113-22-0(937799-91-2)
|
|
Molecular weight:
|
|
434.46
|
|
Purity:
|
|
> 98%
|
|
Appearance:
|
|
White
|
|
Chemical name:
|
|
4-(3-(1-(cyclopropanecarbonyl)piperazine-4-carbonyl)-4-fluorobenzyl)phthalazin-1(2H)-one
|
|
Solubility:
|
|
Up to 100 mM in DMSO
|
|
Synonyms:
|
|
AZD2281, AZD-2281, Olaparib, KU-0059436
|
|
Storage:
|
|
For longer shelf life, store solid powder at 4oC desiccated, or DMSO solution at -20oC
|
References
1. Evers et al., Selective inhibition of BRCA2-deficient mammary tumor cell growth by AZD2281 and cisplatin.
Clin Cancer Res 2008, 14(12), 3916-3925. Pubmed ID: 18559613
2. Senra et al., Inhibition of PARP-1 by olaparib (AZD2281) increases the radiosensitivity of a lung tumor
xenograft. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011, 10(10), 1949-1958. Pubmed ID: 21825006
|
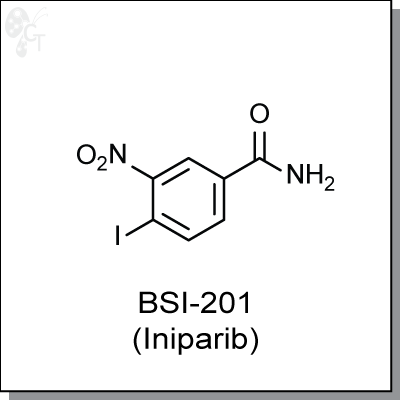
Product Name: BSl-201 (Iniparib) | PARP inhibitor (#C2201)
BSI-201 (Iniparib), a iodonitrobenzamide-based cytotoxic agent, was initially considered to be a PARP
inhibitor based on its abillity to inactivate PARP by means of zinc ejection from the zinc finger of the enzyme.
[1]
Despite its ability to kill normal and neoplastic cells at high concentrations (>40 uM), further studies revealed
that BSI-201 did not selectivly kill homologous-recombination (HR)-deficient cells, sensitize cells to
topoisomerase I poisons, or inhibit PARP in situ, as seen with olaparib and veliparib. [2]
Through a battery of enzymatic, cellular, and viability assays, BSI-201 was shown to nonselectively modify
cysteine-containing proteins in tumor cells. It is also postulated that the formation of nonspecific adducts can
alter stability, activity, and localization, thus inducing apoptosis, stress, cell-cycle perturbation, or DNA
damage. [3]
|
Details
|
Chemical Formula:
|
|
C7H5IN2O3
|
|
CAS No.:
|
|
160003-66-7
|
|
Molecular weight:
|
|
292.03
|
|
Purity:
|
|
> 98%
|
|
Appearance:
|
|
White
|
|
Chemical name:
|
|
4-iodo-3-nitrobenzamide
|
|
Solubility:
|
|
Up to 100 mM in DMSO
|
|
Synonyms:
|
|
BSl-201, BSl201, BSl 201, 160003-66-7, Iniparib
|
|
Storage:
|
|
For longer shelf life, store solid powder at 4oC desiccated, or DMSO solution at -20oC
|
References
1. Mendeleyev et al., Potential chemotherapeutic activity of 4-iodo-3-nitrobenzamide. Biochem. Pharmacol.
1995, 50(5), 705-714. Pubmed ID: 7669074
2. Patel et al., Failure of Iniparib to inhibit poly(ADP-Ribose) polymerase in vitro. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18,
1655-1662. Pubmed ID: 22291137
3. Liu et al., Iniparib nonselectively modifies cysteine-containing proteins in tumor cells and is not a bonafide
PARP inhibitor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 510-523.
|
|




