Bacterial cell wall synthesis enzyme assays
본문
|
Bacterial cell wall synthesis enzyme assays
The following high throughput assays for enzymes in the bacterial cell wall synthesis pathway are available for drug discovery.
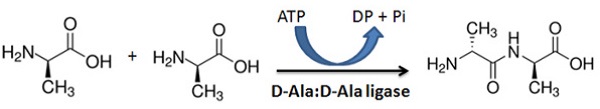
Bacterial D-Alanine : D-Alanine ligase assay D-Alanine-D-Alanine is one of the building blocks in peptidoglycan biosynthesis in bacteria. This dipeptide is generated by ligation between two D-Alanine molecules catalyzed by D-Alanine : D-Alanine ligase. The ligation reaction is coupled to the hydrolysis of ATP forming ADP and inorganic phosphate.
The E. coli D-Alanine : D-Alanine Ligase Assayis based on measurement of the inorganic phosphate generated from the D-Alanine : D-Alanine ligation reaction. The inorganic phosphate is detected by light absorbance at 650 nm. The assay reactions and detection can be performed by using 384-well or 96-well assay plates. Alternatively, the assay reaction can be carried out in Eppendorf tubes and the signal is measured using a cuvette. The high throughput assay can be used for screening inhibitors of E.coli D- Alanine : D-Alanine ligase in drug discovery research. It may also be used for characterization of E.coli D- Alanine : D-Alanine ligase.
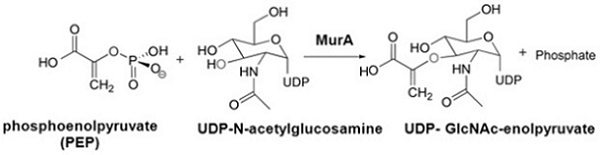
Bacterial MurA Assays MurA or UDP-N-acetylglucosamine enolpyruvyl transferase catalyzes the first committed step in peptidoglycan biosynthesis in bacteria. It is an essential enzyme and attractive target for anti-bacterial drug discovery. MurA transfers enolpyruvate from phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to uridine diphospho-N- acetylglucosamine (UNAG) generating enolpyruvyl-UDPN-acetylglucosamine (EP-UNAG) and inorganic phosphate.
The Bacterial MurA Assay is based on measurement of the inorganic phosphate generated from the MurA reaction. The inorganic phosphate is detected by light absorbance at 650 nm. The assay reactions and detection can be performed by using 384-well or 96-well assay plates. Alternatively, the assay reaction can be carried out in Eppendorf tubes and the signal is measured using a cuvette. The high throughput assay can be used for screening inhibitors of bacterial MurA in drug discovery research. It may also be used for characterization of bacterial MurA.
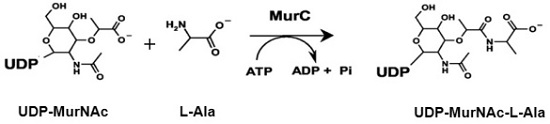
Bacterial MurC Assays MurC or UDP-N-acetylmuramic acid:L-alanine ligase is the first of four paralogous amino acid-adding enzymes in the pathway of peptidoglycan biosynthesis in bacteria. It is an essential enzyme and attractive target for anti-bacterial drug discovery. MurC catalyzes the addition of L-alanine onto the nucleotide precursor UDP-MurNAc generating UDP-MurNAc-L-Ala. The ligation reaction is coupled to the hydrolysis of ATP forming ADP and inorganic phosphate.
The Bacterial MurC Assay is based on measurement of the inorganic phosphate generated from the MurC reaction. The inorganic phosphate is detected by light absorbance at 650 nm. The assay reactions and detection can be performed by using 384-well or 96-well assay plates. Alternatively, the assay reaction can be carried out in Eppendorf tubes and the signal is measured using a cuvette. The high throughput assay can be used for screening inhibitors of bacterial MurC in drug discovery research. It may also be used for characterization of bacterial MurC.
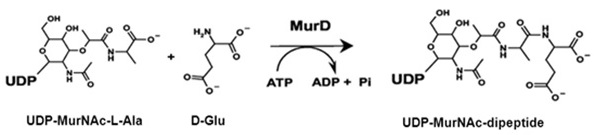
Bacterial MurD Assays MurD is a D-Glutamic acid-adding enzyme in the pathway for bacterial cell-wall peptidoglycan synthesis. It is an essential enzyme and attractive target for anti-bacterial drug discovery. MurD catalyses the addition of D-glutamic acid to UDP-MurNAc-L-Ala, generating UDP-MurNAc-dipeptide. The ligation reaction uses ATP hydrolysis as an energy source forming ADP and inorganic phosphate.
The Bacterial MurD Assay is based on measurement of the inorganic phosphate generated from the MurD reaction. The inorganic phosphate is detected by light absorbance at 650 nm. The assay reactions and detection can be performed by using 384-well or 96-well assay plates. Alternatively, the assay reaction can be carried out in Eppendorf tubes and the signal is measured using a cuvette. The high throughput assay can be used for screening inhibitors of bacterial MurD in drug discovery research. It may also be used for characterization of bacterial MurD.
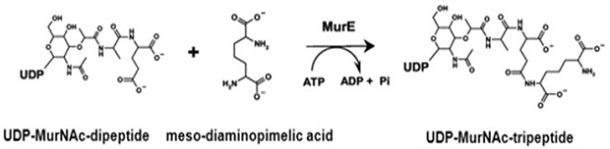
Bacterial MurE Assays MurE or UDP-MurNAc-tripeptide ligase is the third amino acid-adding enzymes in the pathway of peptidoglycan biosynthesis in bacteria . It is an essential enzyme and attractive target for anti-bacterial drug discovery. MurE catalyses the addition of lysine or meso-diaminopimelic acid (DAP) into the MurD product UDP-MurNAc-dipeptide in bacteria generating the UDP-MurNAc-tripeptide. The ligation reaction is coupled to the hydrolysis of ATP forming ADP and inorganic phosphate.
The Bacterial MurE Assay is based on measurement of the inorganic phosphate generated from the MurE reaction. The inorganic phosphate is detected by light absorbance at 650 nm. The assay reactions and detection can be performed by using 384-well or 96-well assay plates. Alternatively, the assay reaction can be carried out in Eppendorf tubes and the signal is measured using a cuvette. The high throughput assay can be used for screening inhibitors of bacterial MurE in drug discovery research. It may also be used for characterization of bacterial MurE.
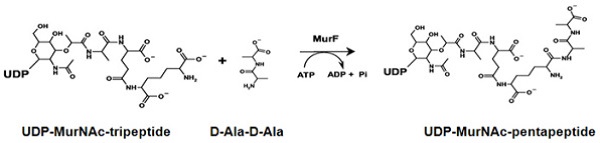
Bacterial MurF assays MurF is the enzyme that catalyzes the last step in synthesis of UDP-MurNAc-pentapeptide in the pathway of peptidoglycan biosynthesis in bacteria. It is an essential enzyme and attractive target for anti-bacterial drug discovery. MurF adds a dipeptide D-Ala-D-Ala onto the MurE product UDP-MurNAc-tripeptide. The ligation reaction is coupled to the hydrolysis of ATP forming ADP and inorganic phosphate.
The Bacterial MurF Assay is based on measurement of the inorganic phosphate generated from the MurF reaction. The inorganic phosphate is detected by light absorbance at 650 nm. The assay reactions and detection can be performed by using 384-well or 96-well assay plates. Alternatively, the assay reaction can be carried out in Eppendorf tubes and the signal is measured using a cuvette. The high throughput assay can be used for screening inhibitors of bacterial MurF in drug discovery research. It may also be used for characterization of bacterial MurF. |
Ordering informations
|
Catalog No |
Product Name |
Size |
|
DDA100KE |
E. coli D-Alanine: D-Alanine Ligase Assay Kit Plus-100 |
100 assays |
|
DDA500KE |
E. coli D-Alanine: D-Alanine Ligase Assay Kit Plus-500 |
500 assays |
|
MURA100KE |
E. coli MurA Assay Kit Plus-100 |
100 assays |
|
MURA500KE |
E. coli MurA Assay Kit Plus-500 |
500 assays |
|
MURC100KE |
E. coli MurC Assay Kit Plus-100 |
100 assays |
|
MURC500KE |
E. coli MurC Assay Kit Plus-500 |
500 assays |
|
MURC100KN |
S. pneumoniae MurC Assay Kit Plus-100 |
100 assays |
|
MURC500KN |
S. pneumoniae MurC Assay Kit Plus-500 |
500 assays |
|
MURD100KE |
E. coli MurD Assay Kit Plus-100 |
100 assays |
|
MURD100KP |
P. aeruginosa MurD Assay Kit Plus-100 |
100 assays |
|
MURD100KS |
S. aureus MurD Assay Kit Plus-100 |
100 assays |
|
MURE100KE |
E. coliMurE Assay Kit Plus-100 |
100 assays |
|
MURE500KE |
E. coliMurE Assay Kit Plus-500 |
500 assays |
|
MURF100KE |
E. coli MurF Assay Kit Plus-100 |
100 assays |
|
MURF100KP |
P. aeruginosa MurF Assay Kit Plus-100 |
100 assays |
|
MURF100KS |
S. aureus MurF Assay Kit Plus-100 |
100 assays |
|
MURF100KN |
S. pneumoniae MurF Assay Kit Plus-100 |
100 assays |
▣ 관련 페이지 ; Profoldin
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.